
Scan Resolution
200nm
S$1778 per sample300nm≤R≤600nm
S$1391 per sample600nm≤R≤1μm
S$1003 per sample>1μm
S$615 per sampleTesting Description
Micro/Nano-CT is a 3D imaging technique utilizing X-rays to see inside an object, slice by slice. Micro/nano-CT scanners capture a series of 2D planar X-ray images and reconstruct the data into 2D cross-sectional slices. These slices can be further processed into 3D models and even printed as 3D physical objects for analysis. With 2D X-ray systems you can see through an object, but with the power of 3D micro/nano- CT systems you can see inside the object and reveal its internal features. It provides volumetric information about the microstructure, nondestructively.
Micro/Nano-CT provides high resolution 3D imaging information that can’t be obtained by any other non-destructive technology. It can be used to study the interior structure of both material and biological samples without having to cut the samples, preserving the samples or specimens for future studies. The quantitative information obtained from micro/nano-CT scanning can only be obtained from 3D images, and 3D digital models created from micro/nano-CT virtual slices allow scientists to measure any parameters for comparison in before-and-after studies.
These unique features of micro/nao-CT scanning allow scientists to look at the morphology of a sample and study features such as: porosity, structure / bone thickness, volume fraction, defect analysis, density, particle size, voids, fiber orientation, etc. Researchers use micro/nano-CT to study bone, teeth, tissue / organs, composite materials, medical devices, batteries, and more.
Sample requirements
Resolution: Refers to the size of the pixel, such as 200nm resolution, that is, the size of a pixel in the picture is a square with a side length of 200nm; assuming that the minimum feature size you want to see is “x μm”, you need to use at least “0.5x μm” resolution.
Sample size: The larger the sample size, the lower the resolution that can be done.
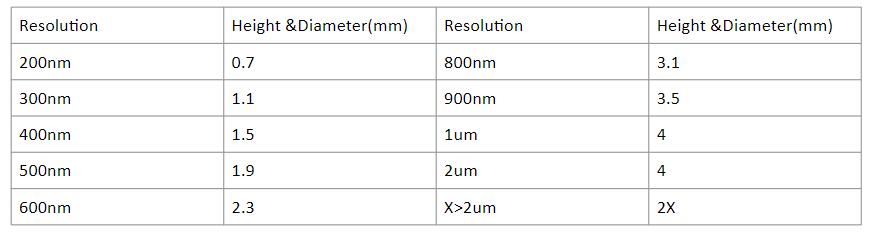
Examples

FAQs
Resources